How to use jupyter notebooks with vs code
As a personal preference, I used a minimal install of Python3 and Pip only and did not install the whole Anaconda package. It would take too much disk space on my mac mini. Of course, it is possible to install Miniconda which has a much smaller footprint. I am happy with Python at the moment, again it is a personal choice. I write this post in case someone can benefit from my set up.
Instead I only installed python 3.8 from python.org and pip from the command line. I created the environment and selected the interpreter in VSCode. This is necessary because macOS comes with a version of Python preinstalled so you do not want to mix the two!
VS Code is a great platform. It is very easy to get started with their excellent support for Jupiter notebooks. As you can see from the screenshot they support dark mode and even have markdown support. The notebook looks really good and can be executed locally.
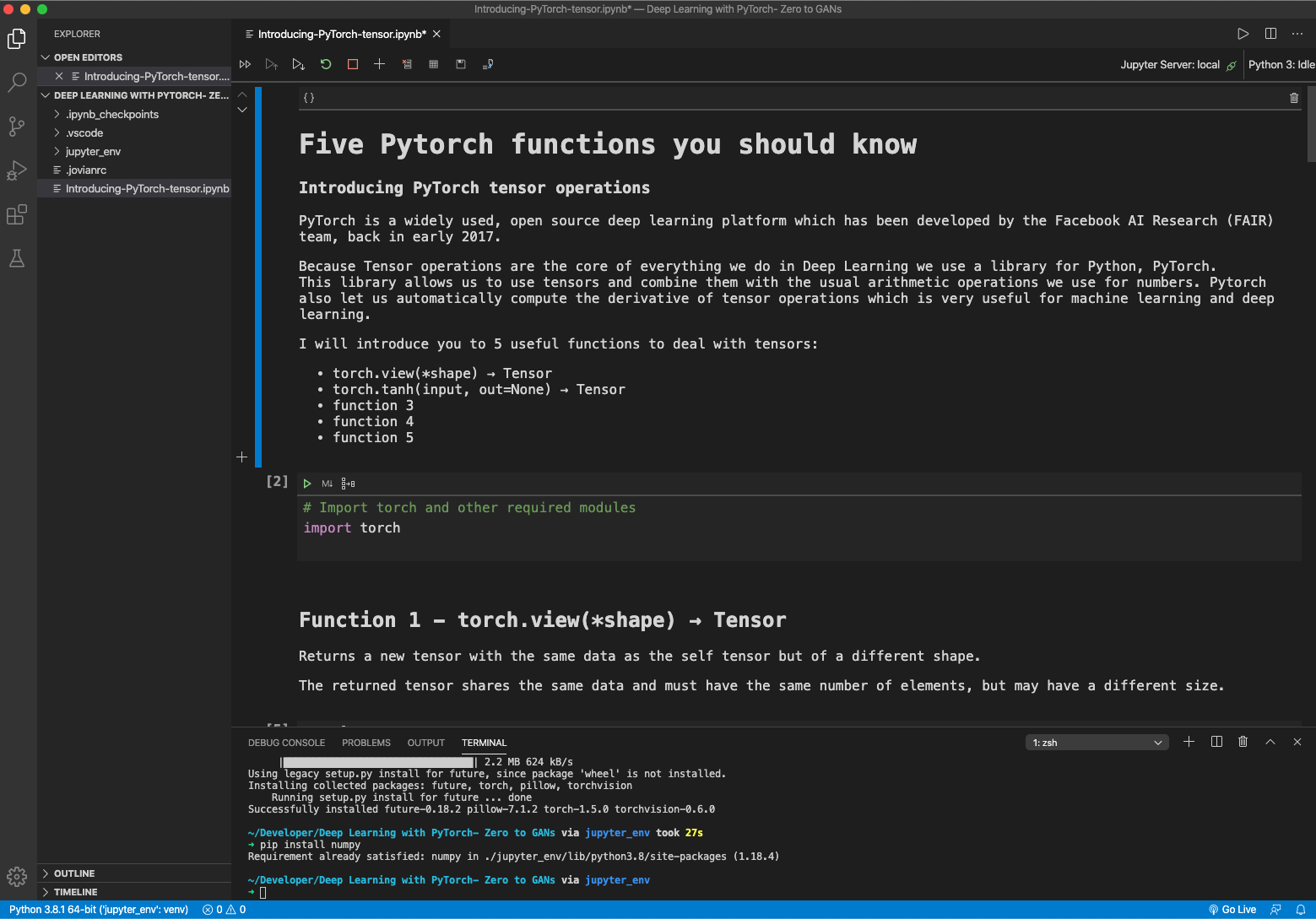
I quote from the VS Code documentation (link is below) :
Jupyter (formerly IPython Notebook) is an open-source project that lets you easily combine Markdown text and executable Python source code on one canvas called a notebook. Visual Studio Code supports working with Jupyter Notebooks natively, as well as through Python code files.
A Jupyter Notebook shows as a webpage in your browser through which you can run python code interactively, and this together with the possibility to preview markdown cells, is the beauty of it.
Create a new folder and set up the environment
(I am on a Mac, on Windows some commands will look different.)
I assume you have already downloaded and installed the latest stable version of python on your system.
Let’s start creating a new folder on your Mac or PC and name it ‘Developer’ or what you like. Then change your current directory to the folder with cd as below:
mkdir Developer
cd Developer
When working with Python, to select your environment is really important. Check your python version with:
which python3
You will need Python3 for everything that has to do with deep Learning. Best is the latest version of Python (3.8).
For every project we create an environment which will allow us to download packages and dependencies in a sandboxed way, this mean that it will not conflict with other versions of python or other packages that we already have in our system.
This can be a life saver and is extremely recommended to avoid ‘dependancy hell’.
We create the environment from the command line:
python3 -m venv <your env name>
For example this was the command for me. I called my environment jupyter_env
python3 -m venv jupyter_env
Then you need to activate it:
source jupyter_env/bin/activate
It will be quite empty when created.
You can check the packages which are in your environment:
pip list
Usually you need to upgrade pip
pip install --upgrade pip
and download the necessary packages for your project:
pip3 install matplotlib
pip install jupyter
pip install jovian --upgrade
pip3 install torch torchvision
Select ther environment in VS Code
In VS Code open the folder as a project with File/Open or File/Open Workspace.
Start to work in the VS Code editor selecting your environment.
To select an environment, use the Python: Select Interpreter command from the Command Palette (⇧⌘P). And select the environment you just created which will have the environment name in it.
The jupyter notebooks
Open the terminal in VS Code with Terminal/New Terminal.
Launch a local server with:
jupyter notebook
This will create a local server and give you the link of the notebook to open it in your browser. Form there you can edit the cells and run your code.
I hope this was helpful. Many people use the Conda package to run notebooks, but the package is a few GBs in size and most people will not need all the functions. This is an easy way to get started, and VS Code is a very powerful and customisable editor.
Jovian.ml
If you use Jovian, go to a notebook, fork it to your profile and click on clone. This will copy a command line command to your clipboard. Paste this in your terminal after have activated your environment. On the Jovian website you will need the API key to sync the changes. Yoiu can run the notebook locally and then sync it to your jovian repo with:
# this if not already installed
!pip install jovian --upgrade --quiet
import jovian
# update with your filename
jovian.commit(filename="Introducing-PyTorch-tensor", environment=None)
# you will be prompted for the API Key
Some resources
The official VS Code documentation: https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/python/jupyter-support
You can see some of my notebooks here at https://jovian.ml/pymultitudes.